The neuroprotective potential of rhubarb in treating traumatic brain injury
07/22/2018 / By Edsel Cook
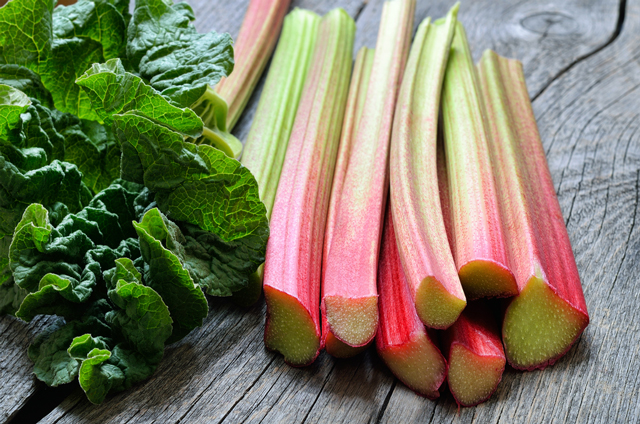

Chinese researchers examined the neuroprotective ability of Rhein, a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) derived from the rhubarb plant. Following their recent animal study, they reported that Rhein was able to protect the brain tissues of rats from oxidative symptoms associated with traumatic brain injuries.
Their study was supported by the Central South University. They published their findings in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
- Rhubarb is used as a TCM for its ability to protect against oxidation. The researchers investigated whether or not the derivative composition Rhein shares this protective property.
- Controlled cortical impact (CCI) rats were given rhubarb. The brain tissue of the animals was analyzed to determine the presence of Rhein.
- Researchers measured the amount of catalase (CAT), glutathione disulfide (GSSG), malondialdehyde (MDA), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) in the brain tissues of CCI rats. They also analyzed the ratio of glutathione (GSH) to GSSG.
- They reported that the brain tissue of the rhubarb-treated rats absorbed Rhein. Both Rhein and rhubarb increased CAT activities, raised GSH level, improved the GSH/GSSG ratio, and increased SOD in those tissues.
- Furthermore, rhubarb and its derivative reduced the amount of oxidation-causing MDA and GSSG. The brain tissues of the treated mice showed less damage from oxidative stress.
Based on the results of their experiment, the researchers suggested that rhubarb and Rhein could possibly serve as neuroprotective agents for humans who suffered traumatic brain injuries. Furthermore, they confirmed that Rhein shared the same antioxidative effect as rhubarb.
The full study can be found at this link. You can read more about herbal medicines that display neuroprotective activities at NaturalMedicine.news.
Journal reference
Xu X, Lv H, Xia Z, Fan R, Zhang C, Wang Y, Wang D. RHEIN EXHIBITS ANTIOXIDATIVE EFFECTS SIMILAR TO RHUBARB IN A RAT MODEL OF TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2017;17(1). DOI: 10.1186/s12906-017-1655-x.
Tagged Under: antioxidant activity, brain health, Brain Injury, brain tissue, food science, herbal medicines, Herbs, medicinal plants, neuroprotective, neuroprotective effect, prevention, research, Rhein, rhubarb, traditional Chinese medicines, traumatic brain injury