A selenium-myo-inositol combination can naturally heal Hashimoto’s disease
05/06/2019 / By Ralph Flores
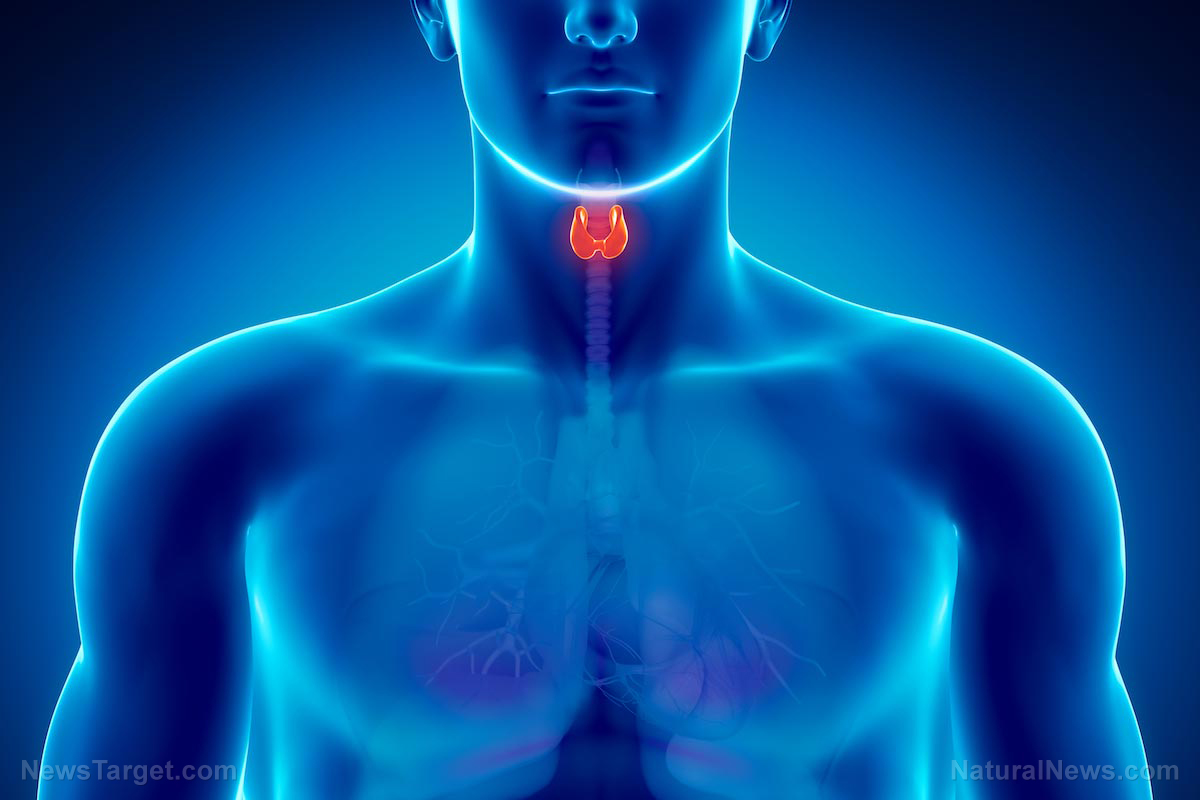
Hashimoto’s disease is one of the most common causes of hypothyroidism in the U.S., affecting at least one out of 20 people. A recent study, however, showed that the combination of selenium and myoinositol can work wonders with people who have this autoimmune condition. The study, which appeared in the journal European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, looked into how this duo can be used to restore normal thyroid function in people with Hashimoto’s disease.
For the study, the researchers recruited 168 patients with Hashimoto’s disease and assigned them into two groups: One group received an oral supplement of myoinositol and selenium, while the other group received selenium alone.
The participants who took myoinositol-selenium supplements exhibited lower levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), anti-thyroid peroxidase (TPOAb) and anti-thyroglobulin (TgAb). TSH, TPOAb and TgAb are biomarkers for autoimmune diseases like Hashimoto’s or Grave’s disease. The reduction in their levels improved the production of thyroid hormones in the participants. In addition, the participants also reported better quality of life after supplementation.
Based on these results, the researchers concluded that myoinositol and selenium supplementation can restore normal thyroid function in people with Hashimoto’s disease.
How does selenium help in improving thyroid function?
Selenium is a rare earth element that confers multiple health benefits. However, taking too much or too little of the nutrient can spell trouble for people.
Mother Nature's micronutrient secret: Organic Broccoli Sprout Capsules now available, delivering 280mg of high-density nutrition, including the extraordinary "sulforaphane" and "glucosinolate" nutrients found only in cruciferous healing foods. Every lot laboratory tested. See availability here.
Based on initial studies, selenium supplementation looks to be a promising treatment for Hashimoto’s diseases. Researchers have shown a link between low selenium levels and the risk of developing the condition. In particular, areas known to have severe selenium deficiency have demonstrated a higher incidence of Hashimoto’s disease.
Selenium, when used with thyroid replacement therapy, can significantly reduce the production of anti-thyroid antibodies, which are overproduced in people with autoimmune diseases that affect the thyroid. A study of over 2,000 pregnant women revealed that selenium supplementation during and after pregnancy can decrease the progression of Hashimoto’s disease and even decrease permanent hypothyroidism.
The benefits of selenium supplementation aren’t just for people with Hashimoto’s disease. Those with Graves’ disease, an autoimmune disease that results in hyperthyroidism, can also benefit from taking selenium.
Myoinositol is essential for thyroid function
Researchers have recently explored the potential of myoinositol as a novel treatment for Hashimoto’s disease. Myoinositol is a vitamin-like substance that is known for its health benefits, especially for diabetics.
A clinical trial involving 86 patients with Hashimoto’s disease showed that taking myoinositol and selenium reduces the number of anti-thyroid antibodies significantly. It also increases the levels of thyroid hormones T3 and T4. In particular, the combination of myoinositol and selenium decreased both thyroid peroxidase (TPO) and thyroglobulin (TG) antibodies, whereas selenium treatment only reduced TPO levels.
By increasing the dietary inclusion of selenium and myoinositol and combining it with regular exercise and a holistic lifestyle, patients with Hashimoto’s disease can find relief from their condition. They can even look forward to having the disease in permanent remission. (Related: Four steps to curing Hashimoto’s disease plus many other autoimmune conditions.)
Looking for foods rich in selenium and myoinositol? Food.news has you covered.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, antibodies, autoimmune disease, disease treatments, Graves disease, hashimotos disease, hypothyroidism, immune system, myoinositol, natural cures, natural medicine, prevention, selenium, selenium deficiency, supplements, thyroid gland, thyroid hormones