TCM’s Yanghe Huayan found to have potent anti-tumor effects against breast cancer
10/14/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez

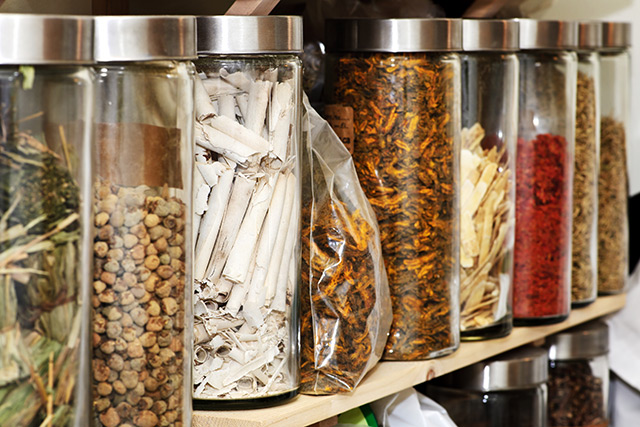
Traditional Chinese medicinal herbs have a long history of use. The earliest record of Chinese medicine dates as far back as the 3rd century BCE. More than 2,000 years ago, the ancient Chinese were already using plant-based treatments to address life-threatening diseases, such as breast cancer. In particular, an herbal preparation called yang he hua yan decoction (YHHY) is widely known as an anticancer medicine for breast cancer. However, the mechanisms behind its ability to stop cancer are still unknown. Hence, researchers from Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine in China conducted a study on YHHY in the hopes of elucidating its anticancer potential. In their study published in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, they discovered that YHHY possesses many chemical components that can delay, and even inhibit, the development of breast cancer.
Breast cancer and YHHY decoction
Breast cancer is a disease that starts when the growth of cells in the breast becomes unchecked. While science is yet to pinpoint the exact cause of this aberration, the development of breast cancer is currently attributed to genetics (family history), hormonal (estrogen, progesterone), or environmental (radiation, tobacco smoke) factors. Breast cancer can be classified as either benign or malignant depending on the ability of cancer cells to invade other tissues and metastasize or spread. Although the majority of breast cancer cases happen in women, breast cancer can also occur in men. (Related: Epigenetics and Breast Cancer: How YOU Can Influence Your Cancer Risk.)

|
Discover how to prevent and reverse heart disease (and other cardio related events) with this free ebook: Written by popular Natural News writer Vicki Batt, this book includes everything you need to know about preventing heart disease, reversing hypertension, and nurturing your cardiac health without medication. Learn More. |
The use of YHHY decoction in the treatment of breast cancer is still prevalent today, especially in Asian countries. YHHY is composed of eight medicinal herbs, which include lu jiao shuang (deer horn fragments), shu di (Rehmannia glutinosa), rou gui (Chinese cinnamon), bai jie zi (white mustard seeds), e zhu (rhizome of Curcuma phaeocaulis), shan ci gu (dried pseudobulb of Cremastra appendiculata), zhe bei mu (bulb of Fritillaria thunbergii), and gan cao (licorice). According to numerous studies, these herbs exhibit various pharmacological activities, not the least of which is anticancer.
YHHY decoction can suppress tumor growth
The development of safe and effective chemopreventive agents is an excellent strategy for reducing the morbidity and mortality of breast cancer. To investigate the mechanism-based chemopreventive potential of YHHY decoction, Chinese researchers used 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene (DMBA) to induce mammary carcinogenesis in female rats. They then orally administered 10 mg/ml YHHY once a day to the animals one week before and four weeks after DMBA treatment. They monitored the development of mammary tumor every day and defined the length of time before the formation of a palpable tumor as tumor-free survival time.
To identify major chemical components of YHHY decoction, the researchers used an adapted high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) protocol. They performed bioinformatics data mining and experimental analyses to demonstrate the underlying mechanism of action of YHHY decoction.
The researchers reported that DMBA-treated rats that received YHHY treatment exhibited a significant delay in tumor occurrence. In some cases, YHHY even prevented tumor development. YHHY decoction also did not show any toxicity in DMBA-treated rats. Instead, YHHY treatment significantly suppressed oncogenic Myc activation. Myc refers to a family of pro-cancer genes that play a role in cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation, and metabolism. In more than 50 percent of human cancers, the expression of the Myc family is deregulated; this deregulation is linked to poor prognosis and survival of cancer patients.
The researchers also identified eight major chemical compounds present in YHHY that interfered with multiple tumorigenic pathways simultaneously. The compounds did the following in mammary tumors:
- Induced tumor apoptosis (programmed cell death)
- Up-regulated pro-apoptotic protein Bax expression
- Down-regulated anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 expression
- Suppressed abnormal cell proliferation and MAPK/ERK, PI3K/AKT signaling
- Blocked new blood vessel formation and the VEGF/KDR signaling
- Inhibited oxidative stress in the mammary tumors
The MAPK/ERK signaling pathway is the most frequently mutated pathway in human cancers, while the PI3K/AKT pathway is an important signaling pathway that contributes to the resistance of certain tumors to anticancer drugs. The VEGF/KDR pathway, on the other hand, is involved in the formation of new blood vessels, which cancer cells rely on to survive, proliferate, and metastasize. Targeting and controlling these pathways are considered important strategies for cancer therapy.
Based on these results, the researchers concluded that the many components and multi-targeting properties of YHHY decoction support its use as a potent chemopreventive drug against breast cancer.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, angiogenesis, anti-tumor, anticancer, apoptosis, Bax protein, Bcl-2 protein, breast cancer, breast cancer mortality, cancer cures, cancer treatment, chemopreventive, disease treatments, herbal medicine, Herbs, malignant tumors, mammary carcinogenesis, medicinal herbs, natural cures, natural medicine, oxidative stress, phytonutrients, prevention, research, TCM, traditional Chinese medicine, women's health, yang he hua yuan decoction